# Introduction to MyScale
MyScale is a cloud-based database optimized for AI applications and solutions, built on the open-source ClickHouse database, allowing us to effectively manage massive volumes of both structured and vector data for the development of robust AI applications. Some of the most significant benefits of using MyScale include:
- Built for AI applications: Manages and supports the analytical processing of structured and vectorized data on a single platform.
- Built for performance: Cutting-edge OLAP database architecture to perform operations on vectorized data at incredible speeds.
- Built for universal accessibility: SQL is the only programming language needed to interact with MyScale.
Compared with other products/platforms' customized APIs, MyScale is simpler to use; thus, suitable for a large community of programmers. MyScale eliminates the need for multiple, costly data warehousing products requiring different query languages with its cost-effective support for data management, superb linear scalability, and standard SQL support. In a single interface, a SQL query can simultaneously and quickly leverage different data modalities to handle complex AI demands that would otherwise require more steps and time.
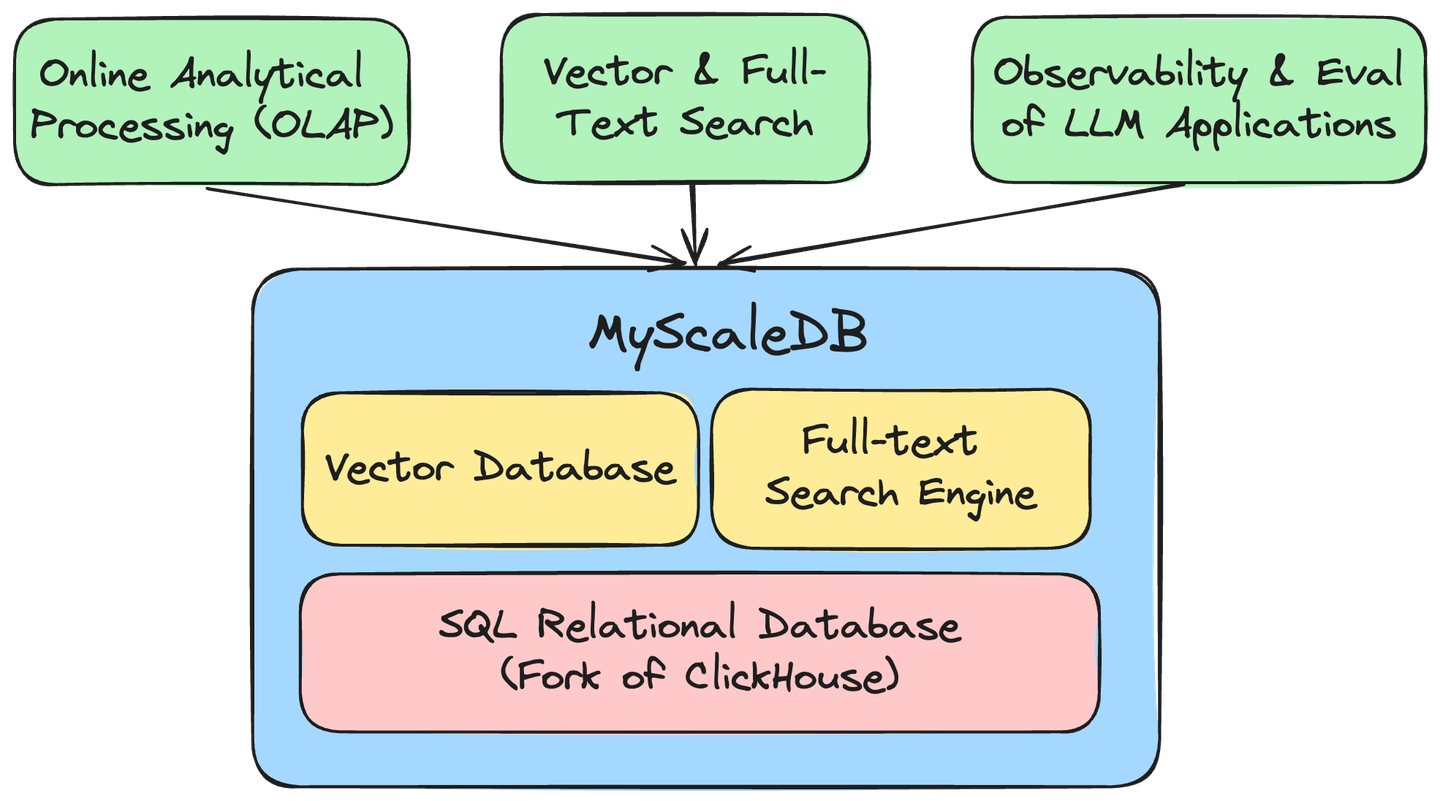
MyScale’s proprietary MSTG vector engine harnesses NVMe SSDs to enhance data density by a factor of 10. This advancement allows MyScale to outperform even the most specialized vector databases (opens new window) by 4x to 10x in both performance and cost-efficiency. The inclusion of a Full-Text Search (FTS) index seamlessly integrates high-performance text search capabilities, positioning MyScale as an efficient upgrade to ElasticSearch (opens new window). Additionally, MyScale Telemetry (opens new window) offers comprehensive observability for LLM systems, ensuring seamless monitoring and efficient debugging.
By integrating the functionalities of an SQL database/data warehouse, vector database, and full-text search engine into a single, efficient system, MyScale significantly reduces infrastructure and maintenance costs. This unification not only facilitates joint data queries and analytics but also establishes a robust and versatile data foundation essential for all AI applications.
# Key Concepts
MyScale is able to perform quick and accurate queries across different data modalities based on the following key concepts.
# Similarity Metrics
There are two different approaches to measuring the semantic similarity between two data objects:
- Unimodal (image-image or text-text): Unimodal similarity measures the semantic similarity between objects of the same data type.
- Multimodal (image-text): Multimodal similarity measures the semantic similarity between objects of different data types.
The semantic similarities between two data objects can be represented by a score known as a similarity metric. Choosing a good similarity metric to represent the semantic similarities in a large database of objects is vital for data classification and clustering performance in MyScale.
Choosing a good similarity metric to represent the semantic similarities in a large database of objects is essential for data classification and clustering performance in MyScale. Three of the more popular metrics include:
- Euclidean distance (L2): L2 is commonly used in computer vision applications (CV) applications.
- Inner product (IP): IP is most often used in natural language processing (NLP) applications.
- Cosine similarity: Unlike IP, which considers the “magnitude” and “angles” that are represented as vectors between two objects, cosine similarity only compares the differences in “angles” on normalized data.
# Search Algorithms
An embedding vector (or vector) is a numerical representation of an object, concept, or entity in a multi-dimensional space. It is often used to represent Natural Language Processing (NLP) texts, IoT sensor data, social media photos, biological and chemical structures, or other data objects in a way that captures their semantic relationships and additional contextual information.
Embeddings are designed to capture meaningful features or characteristics of the data in a lower-dimensional space, making it easier for machine learning algorithms to process and analyze the data.
TIP
Modern embedding techniques are used to convert unstructured data to vectors, transforming high-dimensional data into a more compact and structured form.
To compare the semantic similarity between two objects, you provide the MyScale database with a query vector. MyScale then uses search algorithms like Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) to quickly and accurately return a list of similar vectors to the query vector.
# Using SQL with MyScale
Unlike proprietary vector databases such as Pinecone, Milvus, Qdrant, and Weaviate, MyScale is built on the open-source SQL-compatible, ClickHouse database. There are several reasons for this, including:
- We can provide our users with a feature-rich database by taking advantage of ClickHouse's mature codebase and ecosystem.
- SQL is widely used for managing relational databases. With MyScale's SQL support, developers and data analysts can leverage their existing knowledge and skills, making it easier to integrate and use.
- SQL supports a wide range of data manipulation, querying, and reporting features. Therefore, as MyScale is fully compatible with SQL, users can perform complex queries and analyze data in many different ways.
- As MyScale is built on top of ClickHouse, it provides fast and scalable performance not only for vector search but also for filtered vector search and complex SQL plus vector queries, such as joining vector search results with another table.
# Why Does This Matter?
As complex data grows exponentially, future-proof solutions are needed that can handle newer data modalities, database sizes, and challenges in finding answers to queries. While this is important, it must not come at the expense of computing performance and a lack of integration between different data modalities.
In addition to traditional data formats, MyScale can also handle future data modalities. In MyScale, combining traditional structured data with vector search results in SQL is a powerful approach to tackling complex AI-related questions while maintaining performance.
Read on to discover how MyScale works and how you may integrate it into your solution.
